Patent is a limited, exclusive and a private right which is acknowledged for an innovation and invention which is a product or a process that provides a new way of doing things or provides a new technical solution for problems. Patent grants rights which allow the creator or the inventor to prohibit others from making, selling or using the innovation. Patents make sure that the creation or the invention cannot be commercially made use, distributed or sold without the consent of the patent owner.
The questions that have to be dealt with when a patent protection is required are:
WHERE TO REGISTER A PATENT?
A patent is registered at the Patent office or through national phase PCT application or in the kind of a conventional application which is followed by complete or provisional specifications. It is filled by the first or the true inventor or the legal representative of the inventor. In case the application is filed by the legal representative of the inventor then the proof of the same has to be submitted along with an application.
WHAT KIND OF PATENT CANNOT BE REGISTERED?
According to Section 3 and Section 4 of the Indian patent act the following subject matters are not patentable in India:
- Inventions identified with nuclear vitality
- conceptual thoughts
- laws of nature or anything as opposed to settled natural laws
- physical wonder
- the revelation of any living thing or non-living substance
- the strategy for farming or cultivation
- another type of known substances
- the strategy for playing games
- any tasteful creation
- anything that causes a genuine damage to humans
- creature, vegetation
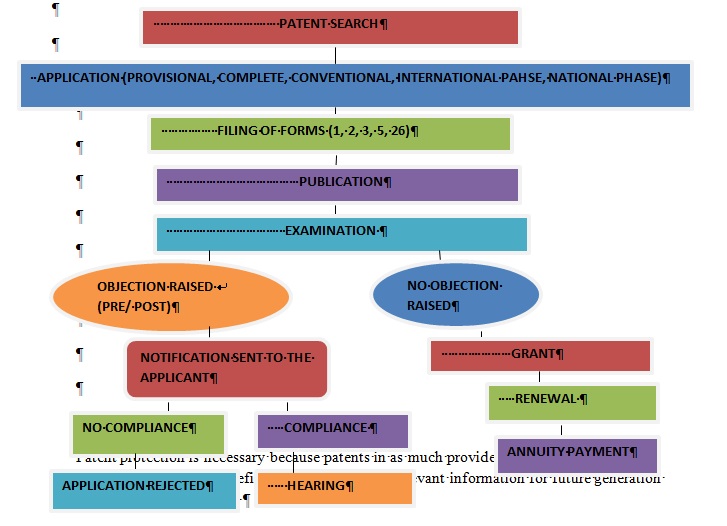
PROCEDURE OF PATENT REGISTRATION IN INDIA
- PATENTABILITY SEARCH: Determining whether the invention meets all the criteria of the patent according the Indian patent act. The invention should be :
- Novel
- Non-obvious
- Industrial applicable
- Enable
- APPLICATION: There are 5 kinds of applications that can be filled in order to register the patent.
- Provisional application: Provisional Application is a brief application documented with a Patent Office to guarantee a “Priority Date” and when a creation is not finished in all viewpoints. This application is to a great degree supportive since it is moderately inexpensive to get ready and record, empowers the creator to consider the achievability of the development as far as potential markets, merchants, licensees. However, the entire application should be recorded in a year or else it will be dealt with as rejected. This application includes:
- Title
- Description in detail
- Drawings, only if necessary
- Sample or model, only if required
- Complete application: A patent application containing the total particular and cases of the development is known as a complete application and this can be documented directly if the innovation is finished in all viewpoints. This application includes:
- Title
- Abstract describing the invention
- Description in detail
- Drawing, only if necessary
- Sample or model, only if required
- Best mode
- Claims
- Deposits, only if necessary
- Convention application: At the point when a candidate making a Patent Filing Application in India, contending a priority date in view of the same or significantly comparable application documented in at least one of the tradition nations, it is known as a traditional or conventional application. Keeping in mind the end goal to get tradition status, a candidate should document the application in the Indian Patent Office inside a year from the date of first recording of a comparative application in the representative nation.
- International application: This application is also known as the Patent cooperation Treaty (PCT) application. It is a universal understanding for documenting patent application in India having an impact in up to 138 nations. PCT does not give concede of a global patent, the settlement:
- Simplifies and postpones the procedure and costs of recording patent applications in the event that one wishes to document in various nations.
- Likewise, the candidate needs to record only a single application with one accepting patent office keeping in mind the end goal to all the while looking for a patent in various (up to 138 nations) over the globe.
- The application is to be recorded in English language inside a year from the date of documented in India.
- Patent cooperation Treaty (PCT) national phase application: An international application made by the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) being the principal application, can enter the national stage in India inside 31 months from the international documenting date or priority date (whichever is prior). This application recorded before the Controller in the Indian Patent Office asserting the need and worldwide documenting date is called PCT National Phase application. The recording date of the application might be the international documenting date agreed under the Patent Cooperation Treaty.
- FILING OF FORMS FOR THE REGISTRATION: There are 5 types of patent application forms which are necessary to be filed:
- FORM 1: Application for the grant of patent
- FORM 2:Complete or provisional specification
- FORM 3: Statement and undertaking by the applicant
- FORM 5:Declaration as to inventor ship
- FORM 26: Authorization of patent agent if the application is filed by the legal representative or agent of the applicant
- PUBLICATION OF THE APPLICATION: After the filing the application, within 18 months the application is published. However the applicant can request for an early publication and in that case the application is published within 1 month of filing it.
- EXAMINATION: The examiner after receiving the application from the controller examines the application in order to determine any defects in the:
- Subject matter
- Novelty
- Non-obviousness
- Enabling
- Industrial application
- Inventive step
- OBJECTIONS RAISED: There are 2 types of objections raised:
- Pre-grant opposition: The opposition which is raised by another party challenging the matter disclosed in the application. There is no essential fee required to be paid to file a pre-grant opposition.
- Post-grant opposition: The opposition raised by another party after the grant of the patent within 1 year of the publication of the patent. The post-grant opposition is to be filed by FORM 7 along with an essential fee of Rs 2400 for a natural person, Rs 6000 for small entity and Rs 12,000 for large entity.
- The applicant against whom the opposition is raise has to comply with it. In case of no compliance the application will be treated as rejected.
- GRANT: After all the formalities the patent will be granted for a time period of 20 years which can be renewed after every year. For the first two years there is no renewal fee but 3rd year onwards an essential fee is to be paid. In case the fee is not paid the patent will be ceased.
Patent protection is necessary because patents in as much provide not only protection for their owners but also beneficial, constructive and relevant information for future generation of inventors and creators.
For getting full and provisional Patent Registration in India Consult Company Vakil and their Expert Trademark Attorneys.

